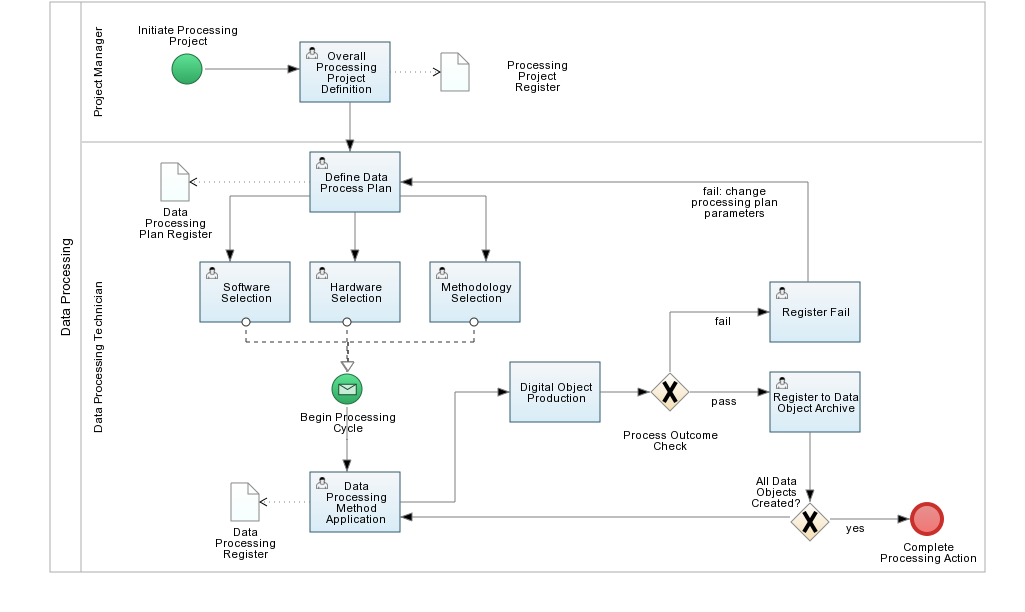
The processing step of a digital survey project takes the results of data acquisition activities and plans for their transformation through various steps using semi-automatic software operations.The results are data products meeting the specifications set out in relation to the initial evaluation of the research question as established in the project initiation step. Since processing can be a complex action with many stages as well as the need for continuous iterative results versus goals validation,we propose a three-tier documentation scheme to track this process: data processing project, data processing plan, data processing action.
The overall documentation unit is a processing project. The processing project is the documentation unit for outlining a sequence of processing actions that will take place according to a controlled data process plan. The processing action indicates the original question to which the processing plan should respond, the products and accuracy it will aim to obtain, and by whom the processing will be organized and controlled. Particularly, the appropriate data objects from the data acquisition activities are selected and documented relative to the objects of study in question. The actual execution of a processing project that will result in the intended end product will require several steps of processing with individual processing plans and iterative processing actions checking for data accuracy and acceptability.
For each distinctive processing step, then, we envision a separate documentation of a data processing plan. The data processing plan lays out the software, hardware and methodology to be employed to achieve the desired effect. Therefore, this data processing plan is attached to the data processing action which has been planned.
Each actual action of processing data under a plan is documented in its own right with the relevant input, output and indicated parameters . What is markedly important is the documentation of the accuracy obtained and therefore, the explicit and documented evaluation by the data processing engineer of the success or failure of the process. Success validates the data processing plan and allows the articulation of the next step of the overall processing project. Failure indicates that the data processing technician should return to the data processing plan and adjust relevant failures and then run the processing actions again until a satisfactory result can be obtained or a negation of one of the relevant factors can be obtained (e.g. software, hardware, methodology or input variables).
| Name | Element |
| Central Register | Processing Project, Processing Plan, Data Processing |
| Supporting Register | Question, Actors, Object, Digital Assets, Equipment |
| Related Control Lists | Processing Type, Algorithm, Accuracy Type, Software, Methodology |